- Sarıgüllük Mahallesi
Mareşal Fevzi Çakmak Bulvarı No: 57/A - Mon. - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed
- Celebral hemorrhage
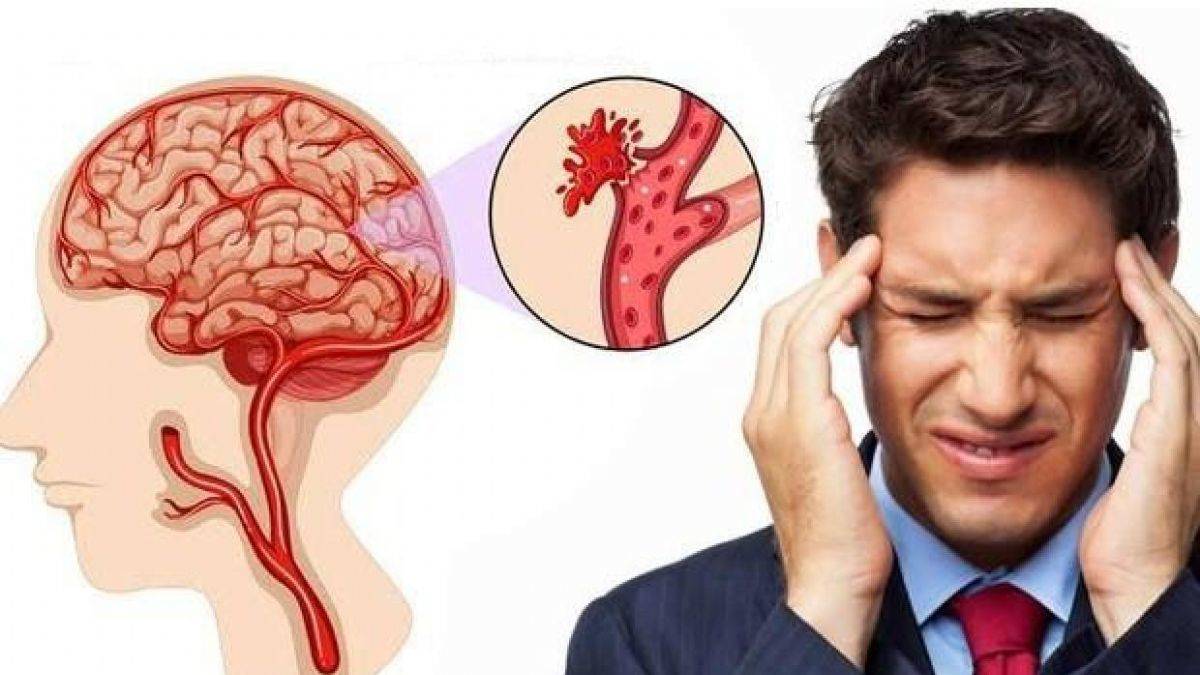
Cerebral hemorrhage is bleeding within the skull, brain tissue, brain cavities and brain surface. It can cause serious injury and death. About 1 million people a year suffer from cerebral hemorrhage.
The most common causes of cerebral hemorrhage are hypertension, congenital vascular disorders of the brain, aneurysm and arteriovenous malformation (a type of structural disorder of AVM-vessels), brain tumors, blood thinners, head traumas, amphetamine and cocaine use in young people.
Subarachnoid Bleeding
Aneurysm bleeding, especially in the brain vessels, is this type of bleeding, and it is usually seen in relatively old people who need to use blood thinners due to a heart disease. The most important symptom is a very severe and sudden onset headache, which is generally described by patients as “the most severe I have ever experienced in my life”.
Subdural Bleeding
Subdural hemorrhages, especially due to head trauma, are caused by the rupture or rupture of the "bridging veins", which are almost suspended between the membranes of the brain. Because the pressure in these veins is relatively low, symptoms can appear between two minutes and two weeks after the event.
Epidural Bleeding
This type of bleeding typically occurs due to fractures of the bones that make up the sides of the skull, called the temporal bone, due to rupture of an artery that runs just below that bone. The most distinctive feature is that, following the loss of consciousness, the patient's consciousness opens for a period of time and then disappears again. This period is called the lucid interval, that is, the "bright period".
Reasons
Diseases and other common causes that increase the risk of brain hemorrhage include:
Hypertension
Chronic high blood pressure, which is the most common cause of cerebral hemorrhage, can weaken the vessel walls and cause bleeding.
aneurysm
It is when a weak area of the vein swells to form a bubble due to blood pressure. Some aneurysms may cause symptoms such as drooping eyelids and visual defects before they burst due to the sensitive areas in their neighborhood. Cerebral hemorrhage occurs when aneurysms rupture.
Head Traumas
It is especially seen after traffic accidents and blows to the head due to falling from a height.
Blood Vessel Anomalies (Arteriovenous Malformations -AVMs)
It refers to certain congenital weaknesses and misconnections in the blood vessels in and around the brain, which can cause bleeding.
Amyloid Angiopathy
It is an abnormality of blood vessel walls that sometimes occurs with aging and high blood pressure. It can cause very small, unnoticeable bleeding before a major one.
Bleeding Disorders
Some coagulation disorders, such as hemophilia, can prevent micro hemorrhages that may occur in the brain from stopping on their own, leading to larger hemorrhages.
Brain Tumors
Tumors in the brain can also lead to cerebral hemorrhage.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a brain hemorrhage can be different for each person. Symptoms depend on the location of the bleeding in the brain, its severity, and the amount of tissue affected. Symptoms can develop suddenly or over time. They can get progressively worse or come on suddenly.
Mild confusion, altered state of consciousness from stupor to coma
Severe headache
Nausea
Vomiting
dizziness
epileptic seizure attack
Disturbances in brain functions depending on the brain area affected by the bleeding
It is not always possible to predict brain hemorrhage. Depending on the area of the brain affected by the bleeding, there may be speech disorder, convulsions in the arms and legs, loss of consciousness, numbness or loss of strength on the right or left side, or paralysis.





 TÜRKÇE
TÜRKÇE ENGLISH
ENGLISH عربى
عربى