- Sarıgüllük Mahallesi
Mareşal Fevzi Çakmak Bulvarı No: 57/A - Mon. - Sat 9.00 - 18.00
Sunday Closed
- Hydrocephalus
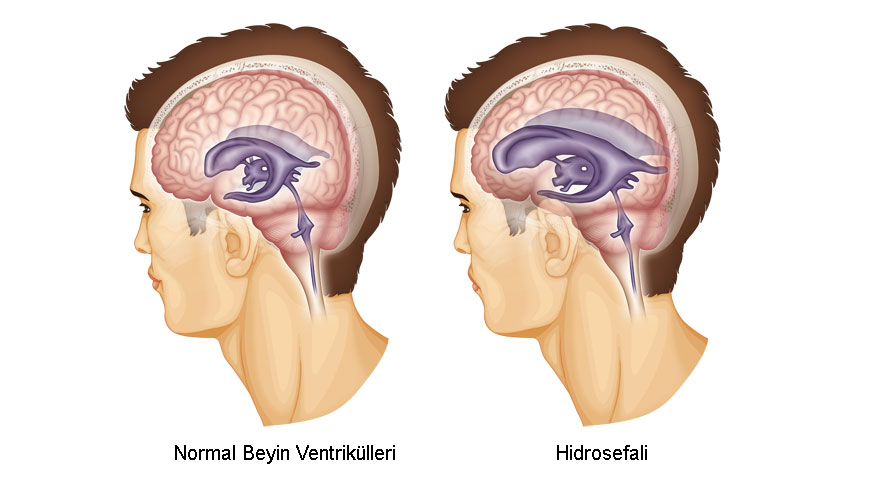
Hydrocephalus is excessive fluid accumulation in and around the brain. The name of the disease consists of the Latin words meaning “water” and “head”. The incidence of congenital hydrocephalus in children is approximately 1 in 500 children. It can also occur in older ages.
This accumulated fluid is called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Most of this fluid is found in fluid spaces (ventricles) inside the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and spinal cord. The blockage of this fluid at one or more points during its circulation and therefore the accumulation of fluid is called hydrocephalus.
CSF provides the brain cells with the nutrients they need and removes waste from the tissues. In this sense, CSF cleans the brain cells. Normally, this fluid is reabsorbed into the blood during the circulation.
In hydrocephalus, there is a problem in the absorption of this fluid, and the fluid accumulates in the brain, causing the skull to enlarge and increase the pressure.
Babies with excess fluid in the brain may experience an enlarged skull and a protrusion on the skull. The increased pressure in the baby's head causes the bones to expand and separate. The baby's head may appear larger than normal.
Hydrocephalus can occur at any age, but most often occurs in children and the elderly (over 60 years of age). Most patients with hydrocephalus are diagnosed at birth, prenatally, or in early infancy. Although rare, it may be due to genetic (inherited) disorders or developmental disorders.
Common Causes of Hydrocephalus
intracerebral hemorrhages, head traumas, brain tumors, hemorrhages due to preterm birth and meningitis. The treatment of hydrocephalus is done by placing a 'shunt' that will allow the fluid to flow into the body, or by draining the fluid.
In summary, a baby with hydrocephalus has extra cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in their brain. The baby's head may appear larger than normal. A healthcare provider can diagnose this condition during an ultrasound in pregnancy.
The goal of treatment is to relieve pressure on your baby's skull. This is done by draining the fluid or reducing its production. The key to treating this condition is early detection, early treatment, and avoiding infection.
Reasons
Causes of Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a rare condition. The buildup of cerebrospinal fluid may be due to a blockage, your baby having trouble absorbing fluid (the bloodstream cannot absorb all the fluid), or, in rare cases, the body producing too much fluid.
Hydrocephalus is congenital or may occur in later ages for other reasons.
Congenital hydrocephalus may be genetic or occur during pregnancy. Possible causes are:
Congenital disorders, these patients constitute the largest group. It may only be hydrocephalus, or it may be associated with other congenital anomalies (meningomyelocele) developing in the spine.
Congenital aquactal stenosis (narrowing or obstruction in the ventricles where fluid circulates in the brain. The cause may be infection, tumor or bleeding in the vein)
Neural tube defects such as spina bifida
Arachnoid cysts: They can block the flow of fluid in the brain
Dandy-Walker syndrome is a condition in which parts of the brain do not develop properly
Chiari malformation: It is a congenital disorder in the nape region where the brain and spinal cord meet.
Early birth
Brain infections or infections in the womb
brain tumors
Intra-cerebral hemorrhages: Brain chambers enlarge after spontaneous hemorrhages.
Birth injuries
The blood vessels in your baby's brain are not forming properly
Head trauma in childhood
Symptoms
Hydrocephalus Symptoms
Each child has different symptoms, and these symptoms may also be due to other diseases. If you see these symptoms, inform your doctor in detail. The definitive diagnosis will be made with detailed examinations by your doctor.
Newborn (0-2 months)
Head growth more than normal
fontanelle swelling
thinning of the scalp
Prominence of the veins in the head
Vomiting
Restlessness and high-pitched crying
Eyes sticking out from their sockets and gazing down
seizures
Baby sleeps too little
The baby is unresponsive
Slow physical and motor development
Children (2 months and above)
abnormal growth of the head
Headache
Nausea
Vomiting
Fire
double vision
Unrest
regression in walking or speaking
communication disorder
Loss of sensory-motor functions
seizures
Older children may have difficulty staying awake or waking up. The large head of the child does not indicate that he has hydrocephalus. The diagnosis is confirmed by MRI. Hydrocephalus is a disease that can be diagnosed in the womb. According to the laws in force, a report to be given by the ethics committee of the hospitals is required for the termination of pregnancy.
Diagnostic Methods
Hydrocephalus Diagnostic Methods
Hydrocephalus can be detected with tests during pregnancy. In the routine ultrasound test during pregnancy, your baby's brain development is followed. Problems such as enlarged ventricles or empty spaces in the brain show up on ultrasound. Barelyk hydrocephalus does not occur in the last trimester (3rd trimester) of pregnancy, so it is not visible in the early ultrasound.
If the baby's brain has these problems, other tests can be done to determine more clearly. Because some babies with hydrocephalus may have other serious health problems, your doctor will order further tests such as Fetal MRI. MRI can be done during pregnancy as it does not contain radiation.
Your doctor may also take a sample of amniotic fluid to check your baby's chromosomes. Chromosome examination is performed with amniocentesis and chondocentesis. A detailed patient history is taken to understand whether there is a neural tube defect in your family.
During routine examinations by the pediatrician after birth, physical and motor development such as head circumference is followed. A family history of the disease is also taken. If your baby's head circumference exceeds the limits that should be according to the month, hydrocephalus is investigated with various tests. With Brain Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Brain Ultrasonography, your baby's brain is displayed in detail.
Treatment Methods
Hydrocephalus Treatment Methods
Although the diagnosis of hydrocephalus can be made in the womb, treatment is not started until the baby is born. Medication is not possible and hydrocephalus is treated with surgical interventions. Selection of hydrocephalus treatment method; It depends on the cause of the obstruction that prevents the circulation of fluid (such as a tumor, cyst), the severity of the disease, your child's age and general health.
While surgery can be performed to remove the tumor and cyst, a surgical method called ETV (endoscopic third ventriculostomy) in which the obstruction in the ventricle is opened can also be preferred by the physician.
In babies diagnosed while in the womb; It is preferred that the baby is delivered as early as possible and the surgery is performed in the earliest period. In patients whose obstruction is not cleared, it is preferred to drain the excess fluid in the brain with a tube 'shunt' method. The goal of treatment is to drain fluid from the brain.
In the surgery, a drainage system called a 'shunt' is placed on the baby's head. This system, which is in the form of a long and elastic tube and has a part called a pump, is placed under the scalp, usually behind the ear.
This system regularly diverts excess fluid to another (heart, lungs, or abdomen) where your baby's body can be absorbed. It does not need a power source such as a battery. The body is able to absorb cerebrospinal fluid. Your doctor will decide on the place of drainage. Thus, excess fluid is drained and intracranial pressure is reduced.
These surgeries are performed by a Pediatric Neurosurgeon specialist, and the post-treatment process and your baby's condition are closely followed by experts from different branches.
The shunt tube, which is barely noticeable from the outside in babies, can be felt on palpation in children and adults.
ETV Method
Another treatment option is ETV (endoscopic third ventriculostomy), in which the obstruction is opened. A Neurosurgeon Specialist enters the brain with a tube with a camera at the end, makes a hole in the atrium and relieves the blockage. Thus, the brain fluid passes through that hole and is absorbed by the blood circulation.
The risks of ETV surgery are sudden closure of the opening after the surgery, infection, fever or bleeding.
Risks of Surgery
The operation is performed under general anesthesia and a small hole is made in the skull and the tip of the shunt is placed where the cerebrospinal fluid is located.
Then, a tunnel is opened under the skin of the head, neck or abdomen, and the other end of the shunt is directed into the heart or abdominal cavity, where this fluid can be easily absorbed.
After shunt surgery, infection, bleeding, short shunt while your baby is developing, and too much or insufficient fluid transfer of the shunt.
Your doctor will follow up closely after the surgery and will adjust the length of the shunt according to the function of the shunt and the development of the child. Therefore, multiple surgeries may be required.
Postoperative
Antibiotic therapy is administered to prevent post-operative infection. After the surgery, your doctors will inform you in detail about your child's care and will tell you about the emergency symptoms you should consider. When you see these symptoms in your child, you should call your doctor immediately.
Post-operative improvement is usually observed. However, if there is permanent damage to the brain tissue, some functions such as vision and intelligence may not improve in your child. The reason for this is the delay in treatment.
A significant portion of patients treated for hydrocephalus can lead a normal life. If you have a child with hydrocephalus and you want a baby again, your doctor may recommend genetic testing. In addition, your doctor will be under close follow-up during your pregnancy.
Effectiveness of Treatment
The effectiveness of treatment for infants born with hydrocephalus depends on how well the shunt request works, as well as on the underlying diseases of the hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus can affect your baby's brain and development. How severe is your child's condition, hydrocephalus?It also depends on other brain diseases and health problems your baby has.
Even if hydrocephalus is treated, it can affect your child's physical and mental development. Your child may need rehabilitation and special education, but a normal life is possible with only a few restrictions. The dependence of the brain on the shunt system may continue for many years. In most patients, removal of the shunt system is not recommended unless it is causing a problem.
Things to pay attention;
In order to prevent the problems that the shunt may cause, it is necessary to go to the examination at regular and frequent intervals.
If your child has the following symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Redness and tenderness at the surgical site and on the shunt line,
restlessness, nausea, vomiting,
Headache, double vision, fever, abdominal pain, convulsions,
Recurrence of preoperative complaints
If these conditions exist, a doctor should be consulted. If problems are not detected and corrected early, dire consequences can occur, which can lead to death. Problems related to shunt can develop very quickly, sometimes within hours. In case of any doubt, it is important to reach the nearest neurosurgery department and/or your doctor who performed the surgery.





 TÜRKÇE
TÜRKÇE ENGLISH
ENGLISH عربى
عربى